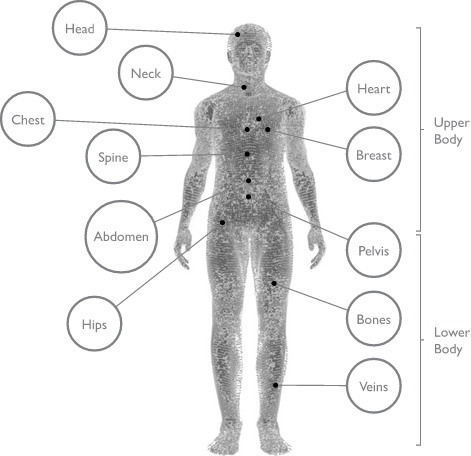
Services
Head to Toe
Procedures for the Abdomen
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Ultrasound Screenings
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) screenings use ultrasound to easily detect these aneurysms. This type of aneurysms usually occur in the aorta, just below the kidneys. The largest of these aneurysms can burst and lead to death within a few minutes.
Barium Enema
A barium enema is an x-ray study that uses a non-toxic contrast liquid to highlight organs, like the large intestine, that need to be studied.
Colon Cancer Screenings: Barium Enemas
Barium enema exams are an alternative for patients who cannot tolerate the sedation required for a colonoscopy. This procedure uses barium to provide contrast inside the colon. X-rays can reveal polyps or other abnormalities.
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
Cystogram
A radionuclide cystogram (RNC) is a test used to determine whether your child has vesicoureteral reflux. This is a condition in which urine flows from the bladder back up to the kidneys.
DMSA Renal Scan
A DMSA renal scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that is used to evaluate the anatomy and physiology of the kidneys.
Gastric Emptying Study
A gastroesophageal reflux study (gastric emptying study) is a diagnostic imaging procedure that measures the time it takes the stomach to empty and helps to detect gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Gastric Emptying Study – Pediatric
A gastroesophageal reflux study (gastric emptying study) is a diagnostic imaging procedure that measures the time it takes the stomach to empty and detects gastroesophageal reflux.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding (GI Bleed)
A GI bleed scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that can help detect the origin of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Hepatobiliary Scan
A hepatobiliary scan (HIDA scan) evaluates the liver, gallbladder and the ducts that are part of the billiary system. It shows the flow of bile from the liver through these ducts, including the gallbladder, emptying in the small bowel.
Hepatobiliary Scan – Pediatric
A hepatobiliary (HIDA scan) scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that outlines the liver, and shows the flow of bile from the liver through the hepatic ducts (including the gallbladder) emptying in the small bowel.
MRE
Magnetic Resonance Enterography (MRE) is a technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret the small intestines. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a method of imaging the body using radioactive materials. Highly skilled professionals use special equipment and procedures to learn how certain organs function and to diagnose and determine the extent of diseases.
Nuclear Medicine – Pediatric
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioisotopes to determine and diagnose disease stages and organ function. This offers the potential to identify disease at the earliest stages as well as responses to therapies.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive imaging modality that helps physicians diagnose and treat many medical conditions. Through the use of sound waves, not radiation, ultrasound images are capable of showing everything from the structure of major organs in the body to blood flow through blood vessels.
Ultrasound – Pediatric
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves – not radiation – to view internal organs and produce diagnostic pictures of the human body. Wake Radiology’s Pediatric Imaging Center is specially designed, equipped and staffed to obtain high-quality ultrasound examinations of pediatric patients of any size, age and medical condition, from tiny newborns to maturing adolescents.
Upper GI
An upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract x-ray procedure examines the esophagus, stomach and first part of the small intestine. A fluoroscopy, special type of x-ray, and an orally ingested contrast material are typically used to obtain quality images.
Upper GI Series (UGI) – Pediatric
An upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract x-ray procedure examines the esophagus, stomach and first part of the small intestine. A fluoroscopy, special type of x-ray, and an orally ingested contrast material are typically used to obtain quality images.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Bones
Bone Density Scans for Adults
A bone density scan is a non-invasive, accurate, inexpensive way of detecting osteoporosis – a chronic condition that occurs when there is a depletion of bone calcium and protein.
Bone Density Screening (DXA)
A non-invasive, accurate, inexpensive way of detecting osteoporosis.
Bone Scan
A bone scan is a non-invasive imaging technique that is used to visualize bones. Different from x-rays or a CT, a bone scan can show bone metabolism. It can be helpful in evaluating damage due to exercise or trauma, bone infection or other causes of unexplained bone pain.
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a method of imaging the body using radioactive materials. Highly skilled professionals use special equipment and procedures to learn how certain organs function and to diagnose and determine the extent of diseases.
Nuclear Medicine – Pediatric
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioisotopes to determine and diagnose disease stages and organ function. This offers the potential to identify disease at the earliest stages as well as responses to therapies.
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation (RFA)
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure to treat atrial fibrillation. Our interventional radiologists consult on this procedure at our partner hospitals.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Breast
3D Screening Mammogram
3D mammography – also called breast tomosynthesis – is performed in conjunction with a traditional 2D digital mammogram. An x-ray arm sweeps the breast taking multiple images that a computer uses to produce a layered 3D image of the breast tissue.
Breast Density
Breast density describes the composition of the breast tissues including fat, milk ducts and lobules as well as glandular and connective tissue. It does not indicate how a breast feels, but instead refers to how it looks on a mammogram.
Breast MRI
Compared to mammography, Breast MRI is a completely different way of looking at the breast. It is an advanced tool using sophisticated computers and 3-D techniques that looks deep into the breast to discover abnormalities that might not be visible in other exams.
Breast Ultrasound
A breast ultrasound uses sound waves to make a picture of the breast including the area closest to the chest wall, which is hard to study with a mammogram. Breast ultrasound is often used to check abnormal results from a mammogram.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
Fast Breast MRI (Abbreviated Breast MRI)
Abbreviated Breast MRI (Fast Breast) is a breast cancer screening tool available to women who have an average risk of breast cancer or who have dense breasts. The benefits of Fast Breast MRI are that it is fast and easy alternative to traditional Breast MRI, scans take less than 20 minutes vs traditional 45 minutes for a Breast MRI. It also requires no prep for the patient and fairly comfortable as images are taken using a large bore MRI machine during the exam. When a traditional Screening Breast MRI is not covered by insurance, a Fast Breast MRI offers a quality alternative for less cost.
Mammogram – Diagnostic
A diagnostic mammogram is typically conducted after a screening mammogram. It is most often used to evaluate abnormal clinical findings, like a lump or atypical area on a screening mammogram.
Mammogram – Screening
Screening mammograms are a powerful tool in the fight against breast cancer, proven to save lives. By detecting breast abnormalities at an early, often more treatable stage, they provide a crucial advantage in the battle against this disease. Wake Radiology’s cutting-edge 3D mammography technology offers a revolutionary way to detect breast abnormalities, providing a more detailed and accurate view compared to traditional 2D mammograms. With 3D mammography, we can identify even the smallest of tumors, reducing false alarms and offering peace of mind for our patients.
Mammography
Mammography is the process of using low-dose amplitude-X-rays to examine the human breast and is used as a diagnostic as well as a screening tool for the detection of breast cancer. Wake Radiology offers both 2D and 3D mammography.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive imaging modality that helps physicians diagnose and treat many medical conditions. Through the use of sound waves, not radiation, ultrasound images are capable of showing everything from the structure of major organs in the body to blood flow through blood vessels.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Chest
CT Lung Cancer Screenings
CT lung screenings help detect and diagnose cancer. Wake Radiology was the first healthcare provider in North Carolina to earn distinction as a Lung Cancer Screening Center by the American College of Radiology. We currently offer lung cancer screenings at six accredited locations across the Triangle.
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
Management of Pleural Effusions and Ascites
Malignant pleural effusions can cause severe shortness of breath and even respiratory failure. Simple drainage of the fluid can be performed on an outpatient basis for relief of symptoms and for diagnosis.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Port Catheter
Central venous access devices are small, flexible tubes placed in large veins for people who require frequent access to the bloodstream. They allow medications to be delivered directly into larger veins, are less likely to clot, and can be left in for long periods.
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation (RFA)
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure to treat atrial fibrillation. Our interventional radiologists consult on this procedure at our partner hospitals.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Head
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
PET-CT
Positron emission tomography, also called PET imaging or a PET scan, is a type of nuclear medicine imaging. Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose or treat a variety of diseases, including many types of cancers, heart disease and other abnormalities.
PET-CT Amyvid Studies
A PET-CT Amyvid (florbetapir) study can help rule out Alzheimer’s Disease. Amyvid is the first FDA-approved agent for PET-CT brain imaging of amyloid plaques in patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer’s and other causes.
Procedures for the Heart
Cardiac Calcium Scoring
Coronary artery calcium scoring (CCS) is a proven, non-invasive, method that can directly identify plaque build up in the coronary (heart) arteries.
CT Coronary Calcium Scoring
Coronary artery calcium scoring (CCS) is a proven, non-invasive, method that can directly identify plaque buildup in the coronary (heart) arteries. Coronary heart disease is the nation’s leading killer and is responsible for more deaths than all types of cancer combined.
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Procedures for the Hips
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MR Arthrogram
An MRI arthrogram, or MR arthrogram, is an imaging procedure that shows the spaces in between joints. The injection of a liquid contrast material into the joint space allows this area to be particularly visible during the MRI.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a method of imaging the body using radioactive materials. Highly skilled professionals use special equipment and procedures to learn how certain organs function and to diagnose and determine the extent of diseases.
Nuclear Medicine – Pediatric
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioisotopes to determine and diagnose disease stages and organ function. This offers the potential to identify disease at the earliest stages as well as responses to therapies.
Ultrasound – Pediatric
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves – not radiation – to view internal organs and produce diagnostic pictures of the human body. Wake Radiology’s Pediatric Imaging Center is specially designed, equipped and staffed to obtain high-quality ultrasound examinations of pediatric patients of any size, age and medical condition, from tiny newborns to maturing adolescents.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Knee
MR Arthrogram
An MRI arthrogram, or MR arthrogram, is an imaging procedure that shows the spaces in between joints. The injection of a liquid contrast material into the joint space allows this area to be particularly visible during the MRI.
Procedures for the Lower Body
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MR Arthrogram
An MRI arthrogram, or MR arthrogram, is an imaging procedure that shows the spaces in between joints. The injection of a liquid contrast material into the joint space allows this area to be particularly visible during the MRI.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a method of imaging the body using radioactive materials. Highly skilled professionals use special equipment and procedures to learn how certain organs function and to diagnose and determine the extent of diseases.
Nuclear Medicine – Pediatric
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioisotopes to determine and diagnose disease stages and organ function. This offers the potential to identify disease at the earliest stages as well as responses to therapies.
PET-CT
Positron emission tomography, also called PET imaging or a PET scan, is a type of nuclear medicine imaging. Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose or treat a variety of diseases, including many types of cancers, heart disease and other abnormalities.
Prostate Artery Embolization
Prostate artery embolization (PAE) is a minimally invasive procedure gaining prominence in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a common condition in aging men characterized by the enlargement of the prostate gland.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Neck
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Thyroid Scintigraphy
A thyroid scan is a diagnostic procedure that produces functional images of the thyroid gland. It can help your physician determine the size, shape and position of the thyroid gland.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive imaging modality that helps physicians diagnose and treat many medical conditions. Through the use of sound waves, not radiation, ultrasound images are capable of showing everything from the structure of major organs in the body to blood flow through blood vessels.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Pelvis
Barium Enema
A barium enema is an x-ray study that uses a non-toxic contrast liquid to highlight organs, like the large intestine, that need to be studied.
Colon Cancer Screenings: Barium Enemas
Barium enema exams are an alternative for patients who cannot tolerate the sedation required for a colonoscopy. This procedure uses barium to provide contrast inside the colon. X-rays can reveal polyps or other abnormalities.
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a method of imaging the body using radioactive materials. Highly skilled professionals use special equipment and procedures to learn how certain organs function and to diagnose and determine the extent of diseases.
Nuclear Medicine – Pediatric
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioisotopes to determine and diagnose disease stages and organ function. This offers the potential to identify disease at the earliest stages as well as responses to therapies.
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation (RFA)
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure to treat atrial fibrillation. Our interventional radiologists consult on this procedure at our partner hospitals.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive imaging modality that helps physicians diagnose and treat many medical conditions. Through the use of sound waves, not radiation, ultrasound images are capable of showing everything from the structure of major organs in the body to blood flow through blood vessels.
Ultrasound – Pediatric
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves – not radiation – to view internal organs and produce diagnostic pictures of the human body. Wake Radiology’s Pediatric Imaging Center is specially designed, equipped and staffed to obtain high-quality ultrasound examinations of pediatric patients of any size, age and medical condition, from tiny newborns to maturing adolescents.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure designed to treat uterine fibroids, which are benign growths in the uterus that can cause various symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on nearby organs. During a UFE procedure, a specially trained interventional radiologist inserts a thin catheter into the blood vessels supplying the fibroids. Tiny particles are then injected to block these vessels, cutting off the fibroids’ blood supply. This causes the fibroids to shrink and often leads to a significant reduction in symptoms
Voiding Cystourethrogram
A voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) procedure uses a fluoroscopy, a special type of x-ray exam, and a contrast material to assess a child’s bladder and lower urinary tract. It is also commonly used for patients with recurring urinary tract infections and urinary reflux following antibiotics or anti-reflux surgery.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Shoulder
MR Arthrogram
An MRI arthrogram, or MR arthrogram, is an imaging procedure that shows the spaces in between joints. The injection of a liquid contrast material into the joint space allows this area to be particularly visible during the MRI.
Procedures for the Spine
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
Kyphoplasty
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive, orthopedic treatment that stabilizes spinal fractures, thereby reducing the pain and correcting the deformity, when possible.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Vertebroplasty
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that helps treat painful fractures involving the vertebral bodies in the spinal column. This procedure uses image guidance to inject a cement mixture into the fractured bone through a hollow needle.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Procedures for the Upper Body
CT Scan
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Wake Radiology’s CT program follows strict dose reduction guidelines for both adult and pediatric CT exams.
CT Scan – Pediatric
CT is one of our most powerful diagnostic tools. These exams combine special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce the CT images. Wake Radiology is the Triangle’s leader in quality images that contain the lowest possible dose of radiation – especially for our youngest patients.
MR Arthrogram
An MRI arthrogram, or MR arthrogram, is an imaging procedure that shows the spaces in between joints. The injection of a liquid contrast material into the joint space allows this area to be particularly visible during the MRI.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an amazing technology that creates images for a radiologist to interpret from the water in your body. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
MRI – Pediatric
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a routine diagnostic procedure that employs strong electromagnets, radio-frequency waves, and powerful computers to generate 2D and 3D images of the body’s organs, tissues and bones. MR imaging does not use radiation to obtain images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a method of imaging the body using radioactive materials. Highly skilled professionals use special equipment and procedures to learn how certain organs function and to diagnose and determine the extent of diseases.
Nuclear Medicine – Pediatric
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioisotopes to determine and diagnose disease stages and organ function. This offers the potential to identify disease at the earliest stages as well as responses to therapies.
PET-CT
Positron emission tomography, also called PET imaging or a PET scan, is a type of nuclear medicine imaging. Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose or treat a variety of diseases, including many types of cancers, heart disease and other abnormalities.
X-ray
An x-ray, formerly called a radiograph, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional x-rays use small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body.
X-ray – Pediatric
Diagnostic X-rays are useful in detecting abnormalities within the body. They are a painless, non-invasive way to help diagnose problems such as broken bones, tumors, pneumonia, and the presence of foreign bodies.